According to studies and research at John Hopkins, approximately 45% of the adult population snores at least occasionally, with 25% snoring all the time. This can disturb the snorer’s sleep, as well as the sleep of their bed partner.
It is important to understand snoring and its health implications. Here is what medical doctors and science tell us.
Who Snores?

Snoring is more common among individuals who are overweight, middle-aged or older men, and postmenopausal women, and tends to worsen with age.
Causes of Snoring
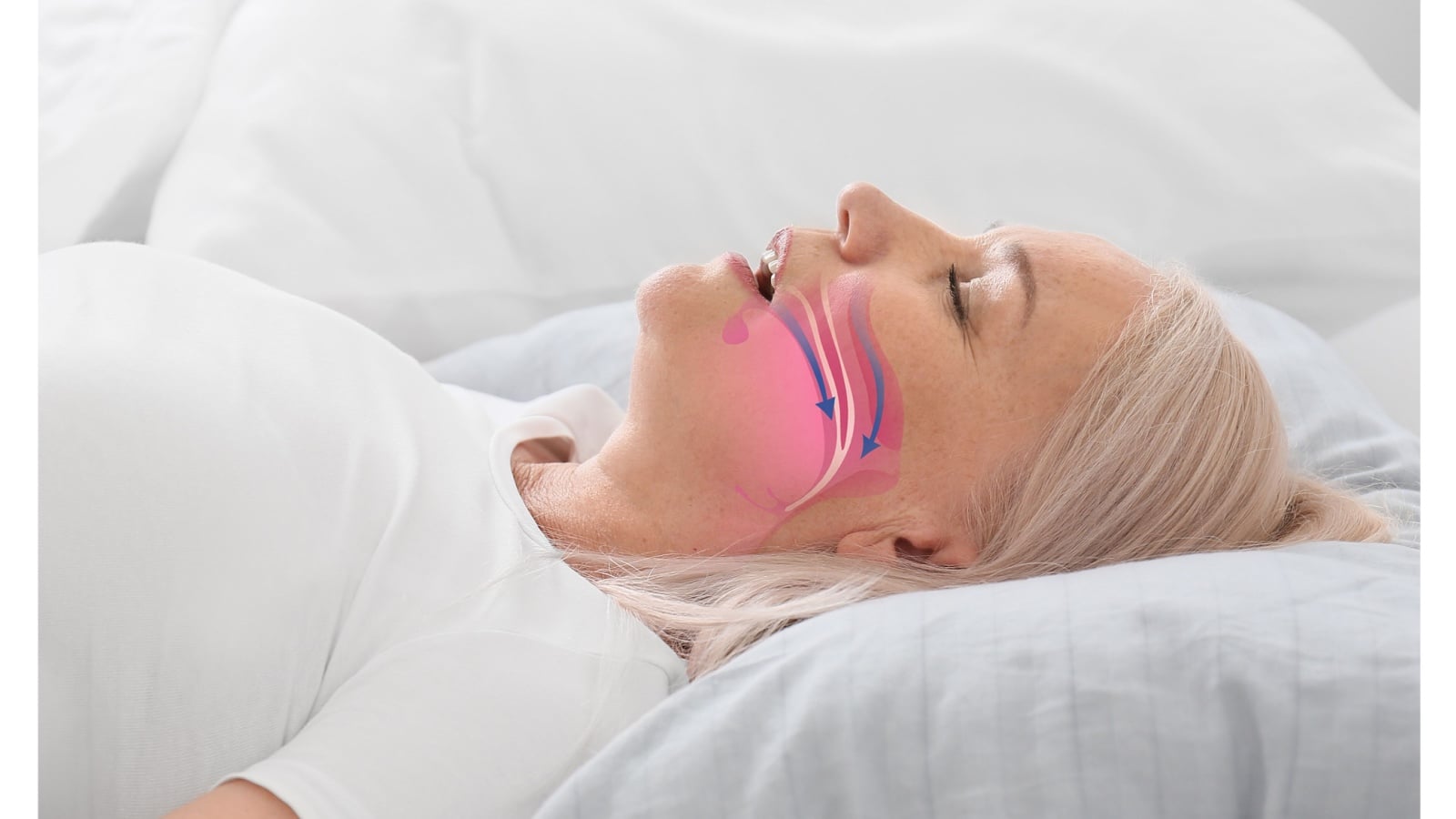

Snoring results from obstructed airways during sleep. Common causes include poor muscle tone in the throat, excessive throat tissue, or an elongated soft palate or uvula.
It can also indicate underlying health issues such as nasal congestion from sinus infections or allergies, nasal polyps, or a deviated septum.
Health Risks Associated with Snoring

While often benign, snoring can signal severe health conditions, including obstructive sleep apnea, which Johns Hopkins sleep specialist Alan Schwartz, M.D., emphasizes as a major cardiovascular risk.
Sleep apnea involves repeated breathing interruptions during sleep, occurring as frequently as 20 to 30 times per hour. These interruptions reduce oxygen levels in the blood and disrupt deep sleep, leading to increased cardiovascular strain and elevated adrenaline levels.
Types of Apnea

There are three main types of apnea:
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA):
This is the most prevalent type of sleep apnea. It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, leading to a blocked airway and preventing air from flowing into the lungs.
2. Central Sleep Apnea (CSA):
CSA arises when the brain fails to send the correct signals to the breathing muscles, causing interruptions in breathing.
3. Treatment-Emergent Central Sleep Apnea (also known as Complex Sleep Apnea):
This condition occurs in some individuals who are initially diagnosed with OSA through a sleep study. During treatment for OSA, such as with CPAP therapy, their condition can evolve into CSA.
These distinctions are crucial for understanding and treating sleep apnea effectively.
Consequences of Sleep Apnea
People with untreated sleep apnea may experience:
- Irregular heartbeats
- High blood pressure
- Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes
- Greater likelihood of developing diabetes
- Elevated risk of accidents due to fatigue
Research indicates that severe sleep apnea can significantly increase the risk of early death in middle-aged or older individuals. Fortunately, treatment with CPAP devices, which maintain open airways during sleep, can mitigate these risks.
What Is CPAP?
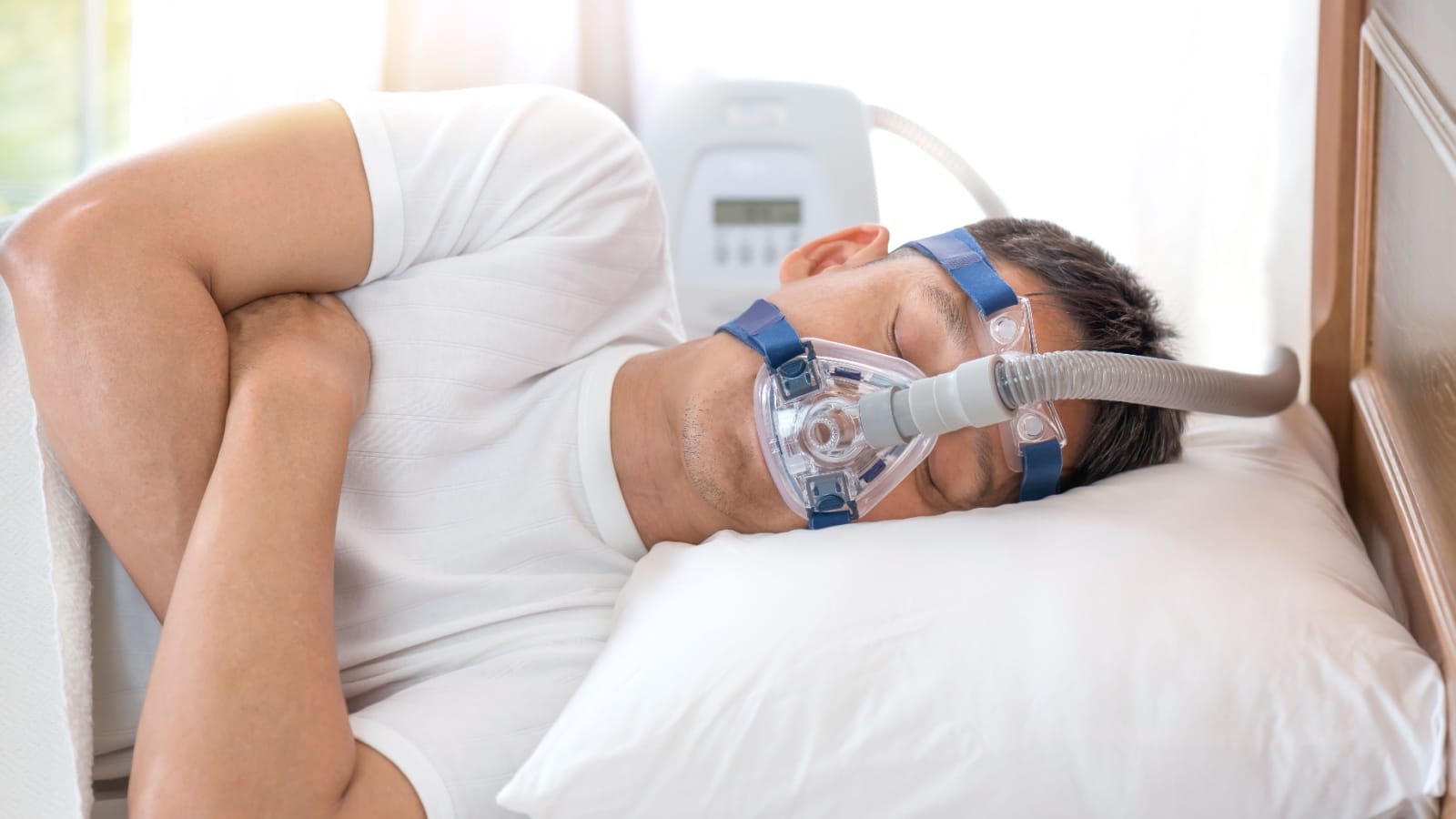

CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) machines use mild air pressure to keep breathing airways open while you sleep. Your healthcare provider may prescribe CPAP to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including sleep apnea.
Structural Issues: Septum, Tonsils & Adenoids
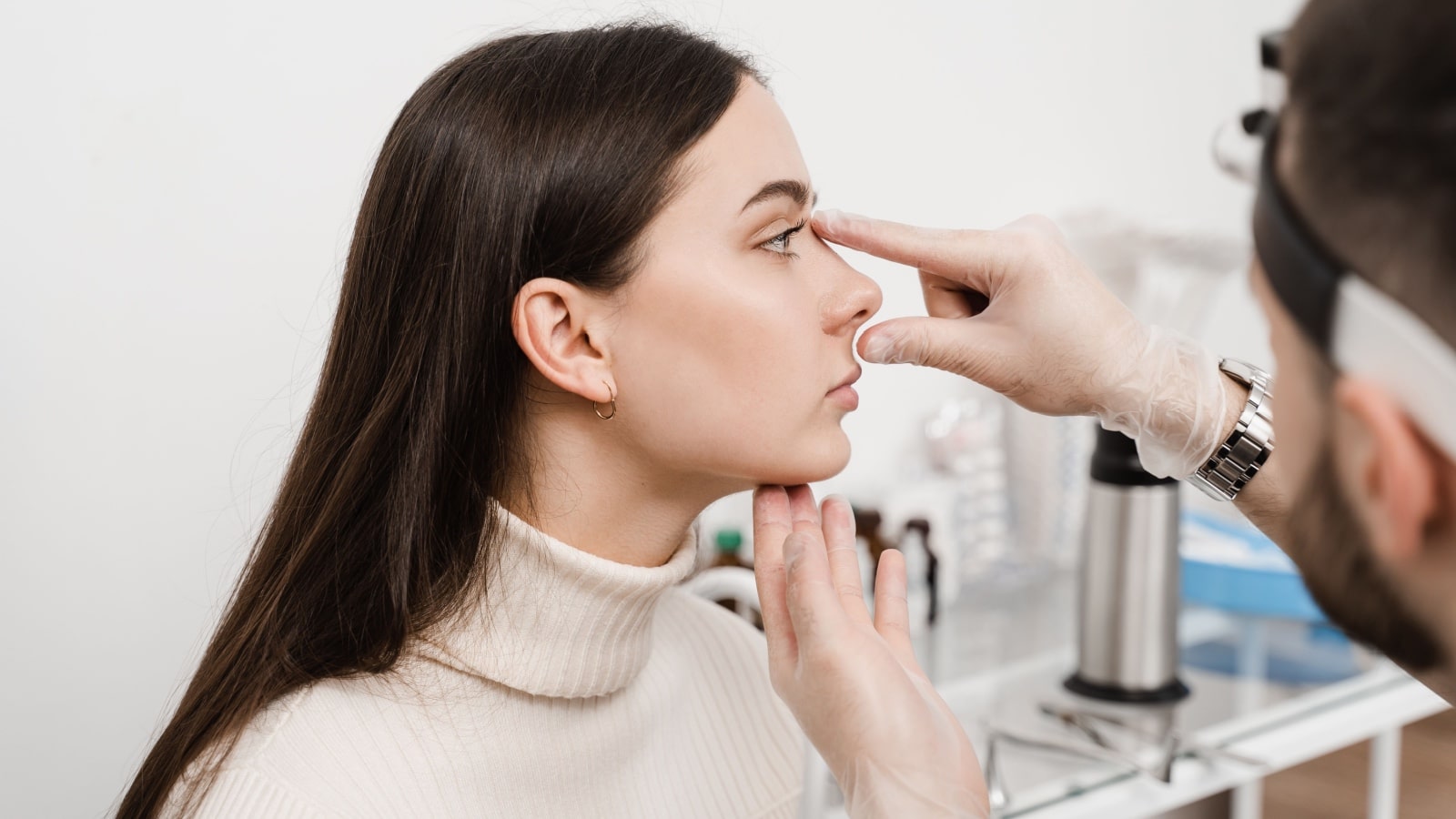

A deviation in the nasal septum can significantly obstruct airflow, exacerbating snoring. Corrective surgery might be considered in severe cases.
Particularly in children, enlarged tonsils or adenoids can block airways, leading to snoring. Surgical removal might be recommended.
Sleep Deprivation from Snoring
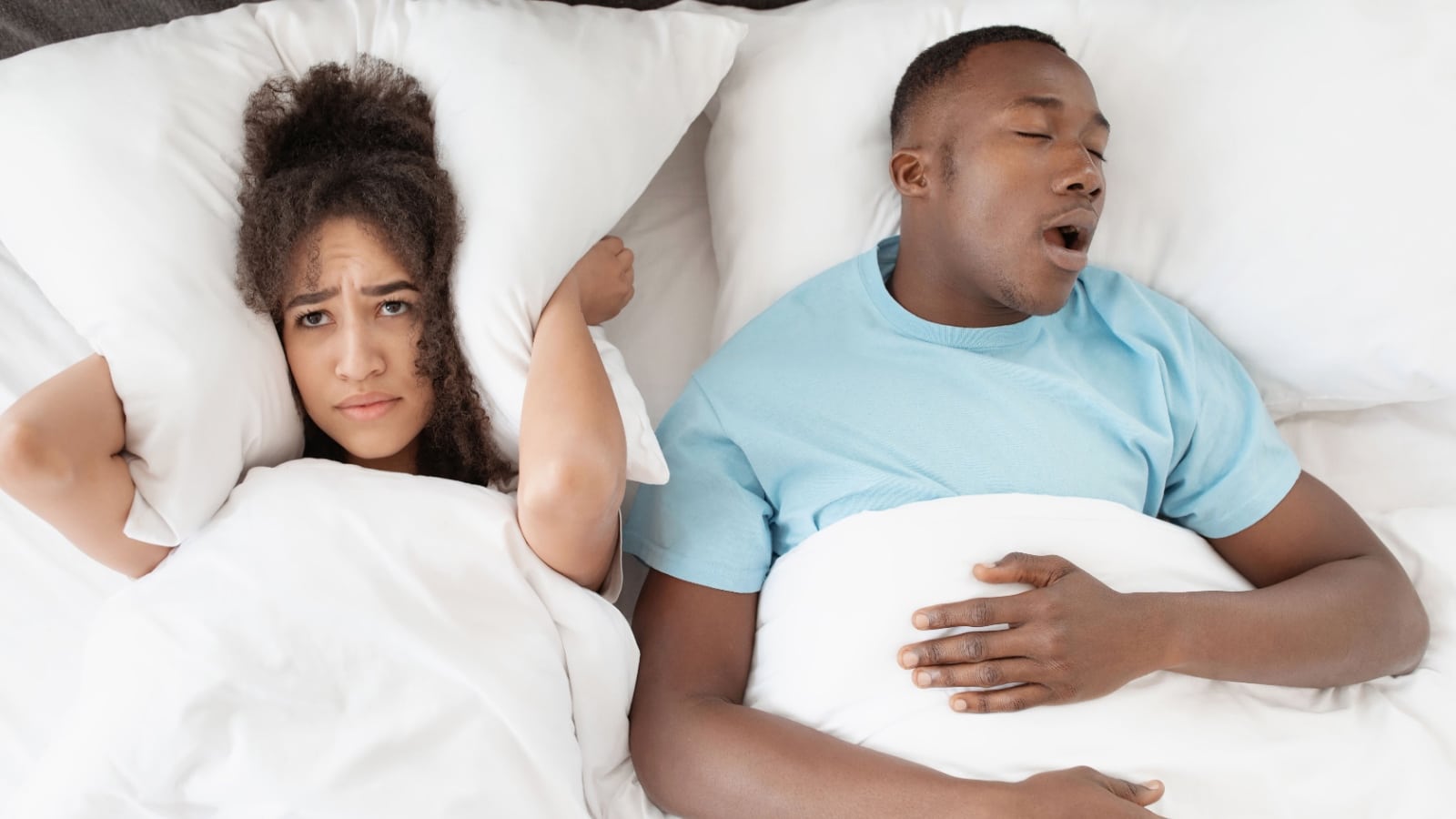

Snoring can significantly disrupt sleep quality and duration, impacting overall health. Adequate sleep supports recovery from illness and injury, and chronic sleep deprivation is linked to numerous health problems, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Moreover, sleep is crucial for mental well-being, affecting stress levels, productivity, and mental health, including risks of depression.
Optimal Sleep Recommendations

Most adults need about 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night to maintain good health.
Addressing Snoring

If snoring affects you or someone close to you, consult a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan to improve sleep quality and address any potential health issues.
To maintain an open airway while sleeping, these self-help strategies are often recommended:
Avoid Alcohol

Refrain from drinking alcohol within three hours before bedtime to prevent your airway muscles from relaxing too much while you sleep.
Medication Caution

Avoid medications that relax your muscles in the evening, particularly benzodiazepines such as alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Klonopin), diazepam (Valium), and lorazepam (Ativan). These are commonly used for anxiety and sometimes for insomnia, but they can relax the throat muscles and worsen snoring.
Weight Management

If you are overweight, reducing weight can help widen your airways. Excess fat in the neck and throat area can narrow these passages, although not everyone who snores is overweight.
Allergies

Allergic reactions can lead to nasal congestion and snoring. Effective allergy management can reduce snoring.
Manage Nasal Congestion

For nasal blockages, try rinsing your sinuses with saline or use allergy medications to reduce dust mites and pet dander. A humidifier may also help reduce nasal tissue swelling.
Stop Smoking

Smoking worsens snoring due to nightly nicotine withdrawal and increased swelling in the upper airway. Even exposure to secondhand smoke can increase snoring.
Optimize Your Bedroom

Ensure a quiet, dark, and cool environment. Use sound machines, blackout curtains, and appropriate bedding to enhance sleep quality.
Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows that support a proper sleeping posture.
Sleep Position

Avoid sleeping on your back as it causes the tongue to block the airway. Try sleeping on your side, supported by a body pillow or with a small fanny pack filled with tennis balls attached to your back to discourage rolling over. Alternatively, elevate your head using an extra pillow or by raising the head of your bed.
These changes and remedies can be effective for simple snoring. However, if you suspect you have sleep apnea, it’s important to consult a doctor.
Behavioral Adjustments

- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s clock.
- Pre-sleep Routine: Engage in relaxing activities, such as reading or taking a warm bath, to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
Have You Had A Sleep Study?
Undergo a sleep study to accurately diagnose issues like sleep apnea.
Get Regular Check-Ups

Maintain regular visits with a healthcare provider to monitor any underlying conditions that might contribute to snoring.
The Takeaway

By addressing both the physical and lifestyle factors contributing to snoring, you can significantly improve your sleep quality and overall health.







